Neuroscience Notes - Sensory Neurobiology
What is a sensory system and what does it do? What is the role of a sensory system in behavior? What are some things that a sensory system does not do?
Terms
| Eng | Chs | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| cochlea | 耳蜗 | |
| incus | 砧骨(位于中耳) | |
| nociception | 伤害感受 | |
| Olfaction | 嗅觉 | |
| Gustation | 味觉 | |
| occipital | 枕骨的 |
Sensory Systems
- Input: Energy contains info about the world
- Accessory structure modifies energy
- Receptor transduces energy into a neural response
- Sensory nerves transfer the coded activity to the central nervous sys
- Thalamus processes and relays the neural response
- Cerebral cortex receives input abd produces the sensation and perception
Hearing
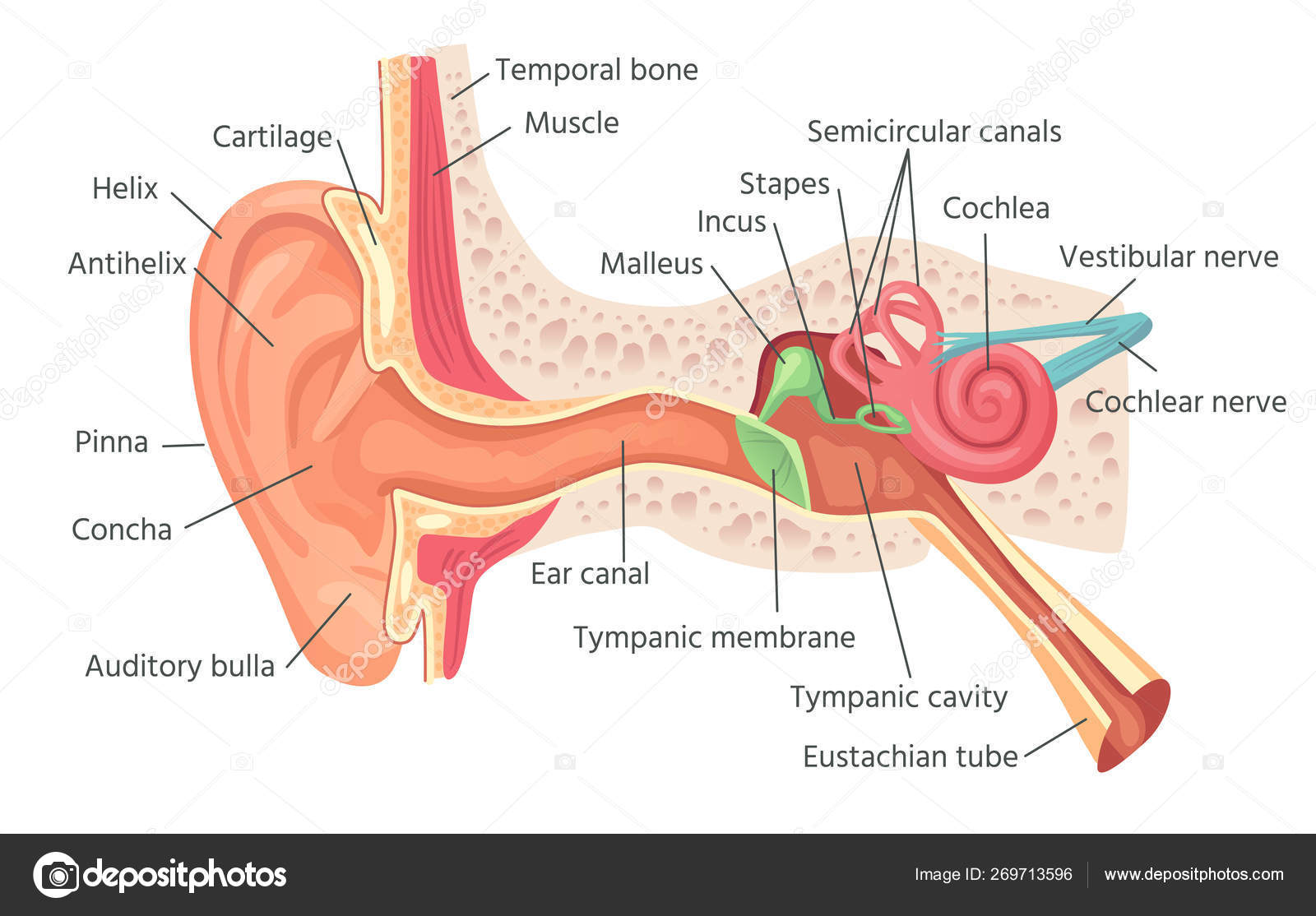
Vibration -> air molecules compression -> tympanic membrane transfer vibrate -> incus -> flow of the liquid in cochlea -> hair cell sense different freq of sound
Auditory System
- cochlea
- auditory nerve
- brainstem
- Thalamus
- Medial geniculate nucleus
- auditory cortex
Somatosense
- Touch Receptors
- Pressure
- Indentation
- Vibration
- Stretch
- Pain receptors (nociception)
- Pressure
- Heat
- Chemical
- Temperature receptors
- Warm
- Cold
- Proprioceptive - kinesthesia (body position)
- Muscle stretch
- Tendon stretch
- Joint movement
- Proprioceptive - vestibular (balance)
- Semi-circular canals (hair cells)
Smell and Taste
- Flavor: taste + smell
- Olfaction: Chemicals in the air
- Gustation: Chemicals in liquid
Taste
- Bitter
- Sour
- Salty
- Sweet
Pathway
- olfactory bulb -> olfactory (piriform) cortex
- taste buds -> 3 nerves -> thalamus -> insula (primary gustatory cortex)
Vision

- Two types of cell: Rod (monochrome) and Cone (RGB)
- Fovea: Small cones only
- Periphery: large cones & many rods


留下评论